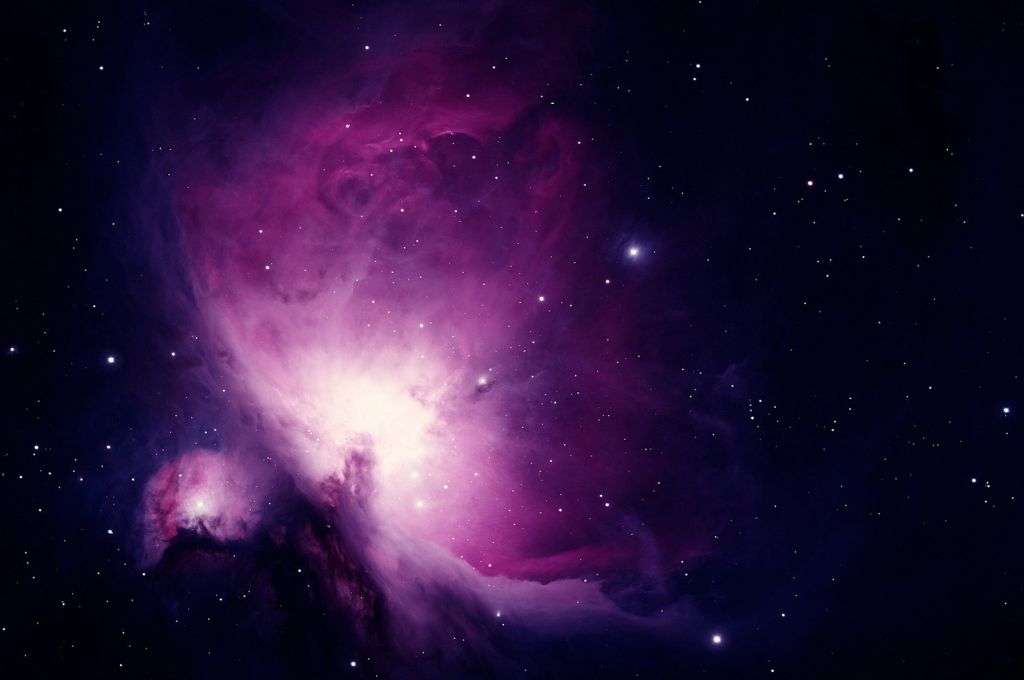
Embarking on a celestial journey beneath the night sky is a thrilling experience. Averted vision, a technique harnessing the subtleties of our eyes’ sensitivity, proves invaluable for avid astronomers seeking to unveil hidden cosmic wonders.
Before delving into mastering averted vision, it’s essential to grasp its foundation—purposefully looking slightly away from the celestial object being observed to leverage the more light-sensitive rods in peripheral vision.
This technique reveals fainter details missed with direct staring. It sounds simple but it’s something that takes a lot of practice, especially for some people.
Now, armed with this understanding, let’s explore nine specific tips on how to use averted vision effectively, including an unconventional one.
Ensure Comfort in Your Astronomy Chair
Beyond optics, your observing comfort plays a crucial role in mastering averted vision. Invest in a comfortable astronomy chair that supports your posture and allows you to relax during extended observation sessions. Being at ease not only enhances your overall experience but also helps maintain focus and attention to detail. Trust me on this one, you don’t wanna skip this.
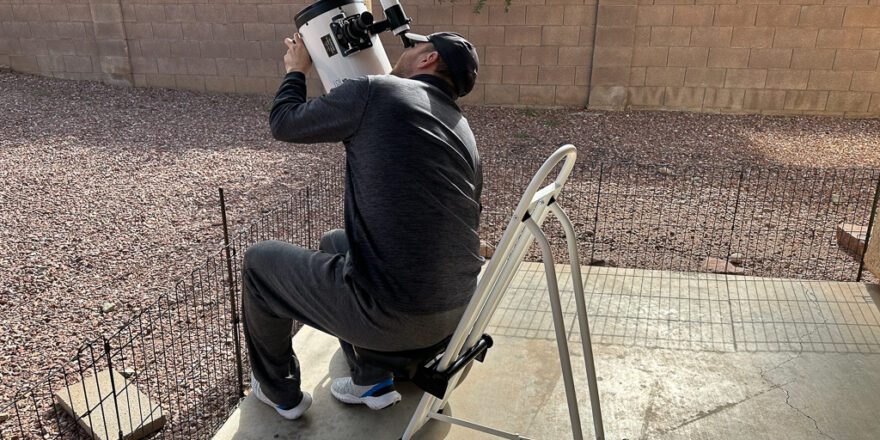

Relax Your Eyes
Start by ensuring your eyes are well-rested and relaxed. The act of stargazing can be surprisingly intense, and tension in the eye muscles can affect your ability to utilize averted vision effectively. Take a moment to blink and allow your eyes to adjust to the darkness before attempting to use averted vision. A few deep breaths can also contribute to a more relaxed viewing experience, enhancing your overall observational capabilities.
Want to get started in astronomy?
Our free telescope cheat sheet breaks down the key factors to choosing a telescope and shows you how to get stunning views of planets, nebula, and galaxies!
Choose the Right Telescope Eyepiece
Opting for the right eyepiece is crucial when employing averted vision. Choose eyepieces with wider fields of view and longer focal lengths (around 12mm to 20mm). Experiment with different eyepieces to find the one that best suits your observing preferences. Specific Example: When observing the Orion Nebula, using a wide-field eyepiece enhances averted vision, revealing the intricate details of the nebula’s glowing gas and embedded stars.
Related: A Beginner’s Guide to Choosing Astronomy Accessories
Peripheral Staring
Mastering averted vision involves training your eyes to use peripheral staring effectively. Instead of fixating your gaze directly on the celestial object, practice looking slightly to the side of it while keeping it in your field of view. This technique maximizes the use of rod cells in your peripheral vision, enabling you to pick up faint details.
For example, when observing the Andromeda Galaxy, peripheral staring helps unveil the faint outer arms and dust lanes, enhancing the overall view. You’ll find out that some deep sky objects are only really appreciated with peripheral vision.
Use Averted Vision in Scanning Motion
When employing averted vision, adopt a gentle scanning motion rather than staring at a fixed point. This technique helps your eyes pick up faint details more effectively. Move your gaze slowly across the object, allowing your peripheral vision to catch elusive features. Just stay relaxed.
Practice Adaptation to Darkness
Spend time allowing your eyes to adapt to the darkness before engaging in serious observations. This adaptation enhances the sensitivity of your rod cells and makes averted vision more effective.
Tip: Consider using a red flashlight to preserve your night vision while consulting charts or adjusting your telescope. Red light has minimal impact on your ability to adapt to darkness, making it an excellent choice for maintaining optimal conditions for averted vision during your stargazing sessions.

Consider Using an Eye Patch
An unconventional but effective tip is to use an eye patch. Covering one eye during observations can enhance averted vision by preventing the covered eye from interfering with the dark adaptation of the observing eye. This not only reduces potential distractions from ambient light but also allows the eye you are using for observing to relax fully. By minimizing the strain on the observing eye and promoting a more focused visual experience, the eye patch becomes a simple yet powerful tool in optimizing the effectiveness of averted vision during your celestial explorations.
Know Your Target
Familiarize yourself with the celestial object you are observing. Understand its features, brightness, and location. This knowledge will help you anticipate what to look for when employing averted vision, making your observations more targeted and rewarding. Knowing the specific details of your target allows you to focus your averted vision on the areas where faint features are most likely to be found. For example, when observing the Ring Nebula, knowing its structure and central star characteristics enhances your ability to detect subtle details using averted vision.
Want to get started in astronomy?
Our free telescope cheat sheet breaks down the key factors to choosing a telescope and shows you how to get stunning views of planets, nebula, and galaxies!

Concluding Your Celestial Exploration
As you embark on your celestial journey armed with the mastery of averted vision, remember that patience and practice are your celestial companions. Each observation session is an opportunity to refine your skills and unlock the secrets scattered across the night sky. Whether you’re scanning the heavens for elusive details or simply marveling at the beauty of the cosmos, averted vision opens a new dimension in your astronomical pursuits. Happy stargazing!